An Emerging Trend
Smart City is a hot and happening concept in the field of urban innovation right now. This concept assumes that a city operates as a system or a group of interlocked parts working together, where technology is used to maximize its efficiency and also unlock its potential, while its chief focus remaining on sustainability.
What makes cities smart?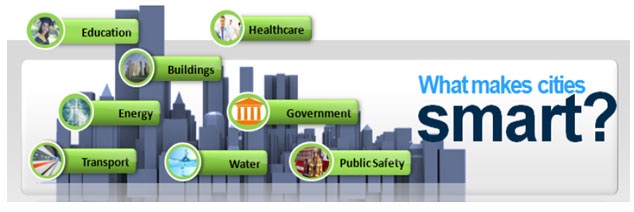
There have been different perspectives about how a smart city should be or what it should have; however there has been no single definition to what makes a city smart. In terms of infrastructure, it focuses around citizen-centric services, the expansion and enhancement of transportation networks, the management of public safety, waste and energy resources, and education and health services. Economic development, tourism promotion, and job creation are also important aspects to be considered.
Technology advancements in the last decade have created the right environment for Smart City solutions. Pervasive wireless and broadband connections, advanced analytics software, intelligent sensors, the profusion of mobile devices, and the use of social media can all be integrated by vendors to provide solutions for city governments.
Global Trends
It is estimated that the smart city market worldwide would be valued at 400 billion USD by 2020 . As it is projected that around 60% of the global population will be in urban locations by 2025, the concept of Smart Cities has started earning acceptance among policy makers.
Urbanization as a trend will have diverging impacts and influences on future personal lives and mobility. Rapid expansion of city borders, driven by increase in population and infrastructure development, would force city borders to expand outward and engulf the surrounding daughter cities to form mega cities, each with a population of more than 10 million. By 2023, there will be 30 mega cities globally, with 55 percent in developing economies of India, China, Russia and Latin America. The mega cities from emerging economies will witness a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.4 percent in GDP (PPP) from 2009 to 2025, as compared to a CAGR of 1.63 percent for the same period in the mega cities from developed economies.
The explosive population growth and dynamic shift in urban sprawl, coupled with the economic growth of mega cities in the emerging economies, will pose a variety of opportunities for companies operating in different sectors. The mega cities from the emerging economies will become the largest markets for existing premium products and technologies, while their developed counterparts will witness a trend of sustainable measures. This will also lead to the evolution of smart cities with eight smart features, including Smart Economy, Smart Buildings, Smart Mobility, Smart Energy, Smart Information Communication and Technology, Smart Planning, Smart Citizen and Smart Governance. There will be about 40 smart cities globally by 2025.
Smart Technologies
Many international firms like IBM, Cisco and Hitachi have been developing innovative solutions for implementing technology in various fields like energy management, water management and much more..
Intelligent water system Concept
In an intelligent water system, treated wastewater that would have been discarded previously is aggressively utilized in residential and industrial areas as recycled water. In addition, the operational data from each water treatment plant is managed centrally as water infrastructure information, thereby enabling efficient operation of each facility. These systems along with various other similar systems can be used in combination in order to provide a solution that can resolve the water shortage problem.
Smart Grid
Electricity generated in power stations reaches us through the power grid. As there has been progress in deploying Renewable energy controlled by the weather, such as wind and solar power generation, it is expected that there will be growth in power demand for applications such as the widespread use of electric vehicles. With a Smart Grid, these sources and demands can be controlled by information technology, enabling us to make deft use of natural energy alongside nuclear power and other conventional power sources, which will help to reduce CO2 emissions.
Smart Mobility
Smart Mobility involves the integration of transportation services along with the implementation of IT services to provide an easier and more efficient way of commuting within the city. With the help of navigation services, the traffic is monitored and the best mode of transport is suggested to the user after simulating the time of travel for each mode. This saves time for the user and enables an energy efficient management of public transport.
Smart Cities in the GCC
In the GCC, the trend of linking smart cities to the agenda of economic diversification is fast gaining ground. Initiatives have been taken in the GCC region, with three countries announcing projects for future Smart Cities: six greenfield economic cities in Saudi Arabia (complemented by efforts to uplift cities such as Mecca toward Smart City status); three projects in Qatar (Lusail’s Smart and Sustainable City, Pearl-Qatar Island, and Energy City Qatar); and two projects in the UAE (Masdar City in Abu Dhabi and Smart City Dubai).
There have been heavy investments across the GCC countries towards smart city projects. According to Cisco, Saudi Arabia has invested USD 70 billion to build four new Smart Cities in a collaborative partnership between the KSA and the Cisco. Spending on IT products and services alone in the Middle East will increase 7.3% year on year in 2014 to top USD 32 billion . IDC expects the total spending on machine-to-machine (M2M) connections in the GCC countries to increase 19% year on year in 2014 to reach $224 million.
Dubai Smart City
The strategy features six key pillars and 100 initiatives on transport, communications, infrastructure, electricity, economic services, urban planning. Under the strategy, 1000 government services will go smart in the next three years. The strategic plan is based on three basic ideas namely communication, integration and cooperation. These ideas will enhance communication between the residents of the city and its institutions. They also facilities easy access and sharing of data about the city to keep them informed about government entities, schools, hospitals, roads and transport, sensor systems, buildings, energy and others.
As part of the Dubai Smart strategy, Roads and Transport Authority will implement a comprehensive plan to ensure access to provide the smart transportation by creation of a ‘unified control center’ for all means of transportation, as well as providing more than 200 services, using smartphones at the end of 2015, in addition to RTA’s current services.
With regard to the energy sector, a number of initiatives including the development of ‘smart electrical grid’ to encourage owners of houses and buildings in Dubai to use solar energy and sell the surplus to the government through the network itself , as well as ” smart meters ” that contribute to rationalizing the consumption of electricity and water are being developed. Dubai Municipality (DM) is working on the implementation of smart parks and beaches projects that provide specific information on weather conditions, sea, temperatures and safety guidelines, as well as the launch of ‘I-Dubai’, which provides information relating to the services of the municipality.
Mecca Smart City
Mecca, one of Islam's holiest cities, is being turned into a smart city through a massive upgrading exercise carried out by the Saudi Arabian government since the end of last year's Haj season. The plan that includes housing, transportation, shopping and historical sites will ensure that Muslims from all over the world can have a safe and nice journey when they perform Haj or Umrah in this holy city.
Two mega projects for road construction and public transportation network are being undertaken for the city as a whole, besides special projects such as the expansion of the Masjidil Haram (Grand Mosque). Certain parts of the great mosque have been under expansion since last year. It can now accommodate 400,000 people for prayers during this Ramadan. The three-year expansion work started just after Haj in mid-November last year. When the whole expansion project is completed, the capacity will be for more than 1.5 million people up to a total of almost two million.
Lusail Smart City
The Lusail Smart City positions itself as one of Qatar’s most advanced cities. Lusail will provide a switched on, high-technology environment comprising both wired and wireless communication networks to offer advanced services.
An operation control centre, based in Lusail City will be responsible for implementing and managing the strategic information technology network covering the city’s entire systems and activities, handling the surveillance systems in and around the city and also maintaining the security of buildings, facilities and streets. Lusail Smart City also offers various telecommunication services for the benefit of citizens and also to encourage business.
Emerging Technology trends in GCC Smart Cities
Governments have been investing in technology to provide innovative solutions for a variety of domains. Most of them are centered on devices like smartphones and tablets. Nearly 75% of people in the UAE own a smartphone. Data from Google suggested that this was the highest level of smartphone penetration in the world, just ahead of South Korea. Saudi Arabia came third, with 72.8% of KSA’s population owning a smartphone.
Dubai government presented its vision for the smart city where government services are to be provided seamlessly to the citizens through technology. It included aspects like citizens wearing smart wrist band to communicate with the government and parents receiving updates on their children’s school results via a digital box at the breakfast table. The smart wrist band would also have several functions where users can use it as a digital passport, digital car key etc. The future of Dubai Smart City will be based on technology to make living more comfortable.
Works have also been going on to implement technology in various day to day services. UAE proposes drones to deliver ID cards and driving licenses. This is a measure taken to save time, increase effectiveness and to make services easier. Ambulances in Qatar could be able to control traffic lights using new technology which will enable emergency vehicles to transmit a signal to change the traffic lights ahead of them. This move could potentially reduce life threatening delays. Google Street View-cars are coming to the Middle East, with Dubai being the first city in the region to have street views added to Google’s online mapping service.
GCC countries are also planning to implement waste containers that are able to communicate with trash disposal services when overflowing, including sending a tweet message. Overflow of waste in trash can has been a constant nuisance for city sanitation departments, landlords and private waste management companies. By monitoring waste containers with smart wireless sensors, collection of garbage can be scheduled and the process can be made more efficient.
Therefore with the rapid advancements in technology and the commitment of GCC governments towards, we may soon be seeing several smart cities in the GCC creating benchmarks for the cities worldwide.